What Is The Difference Between Angioplasty and Angiography?
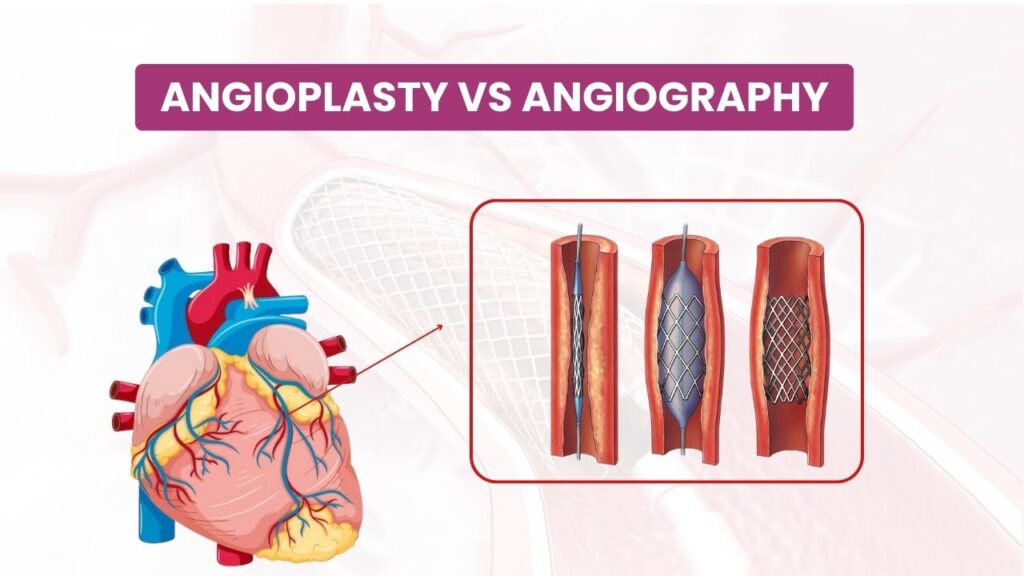
When it comes to heart health, understanding the distinction between angioplasty and angiography is crucial. While these terms sound similar, they refer to different procedures used in diagnosing and treating cardiovascular issues. Let’s explore what each procedure entails and highlight their key differences. What is Angiography? Angiography is a diagnostic procedure that provides detailed images of the blood vessels and the heart chambers. It’s primarily used to identify blockages, abnormalities, or other issues within the blood vessels. Purpose: Angiography helps doctors detect conditions like coronary artery disease, aneurysms, and blood clots by visualizing the blood vessels. Procedure: A contrast dye is injected into the bloodstream through a catheter inserted into an artery, typically in the groyne, arm, or neck. As the dye travels through the blood vessels, X-ray images are taken to reveal any blockages or irregularities. Preparation and Recovery: Patients may need to fast before the procedure. Angiography is usually done on an outpatient basis, allowing patients to go home the same day, though they might need someone to drive them. Risks: While generally safe, angiography carries risks such as allergic reactions to the dye, bleeding, or damage to blood vessels. What is Angioplasty? Angioplasty, or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a therapeutic procedure designed to treat narrowed or blocked arteries, especially in the heart. Purpose: The goal of angioplasty is to open up narrowed or blocked arteries to restore proper blood flow to the heart muscle, often necessary in cases of coronary artery disease. Procedure: A catheter with a small balloon on its tip is inserted into an artery, usually in the groyne or wrist. The catheter is guided to the site of the blockage, where the balloon is inflated to compress the plague against the artery walls, thus opening the artery. To maintain the artery open, a stent is frequently implanted. Preparation and Recovery: Preparation involves fasting and possibly adjusting medications. Recovery may require a hospital stay for a day or two for observation, especially if a stent is placed. Risks: Risks include artery damage, bleeding at the catheter site, and, rarely, heart attack or stroke during the procedure. Key Differences Purpose: Angiography is used for diagnostic purposes to visualize blood vessels and identify problems, whereas angioplasty is a treatment method to open up blocked arteries. Procedure: Angiography involves injecting dye and taking X-rays to view blood vessels, while angioplasty involves inflating a balloon to clear blockages and placing a stent. Outcome: Angiography provides diagnostic images, while angioplasty directly addresses the blockage to improve blood flow. Conclusion Both angiography and angioplasty are vital in managing heart conditions. Angiography helps doctors diagnose cardiovascular problems by providing clear images of the blood vessels, while angioplasty offers a solution by restoring proper blood flow through the arteries. Knowing these processes will enable you to make well-informed judgements on the condition of your heart. Always consult with your healthcare provider for advice tailored to your specific medical needs. Your heart health is important, and knowing the appropriate procedures can make a significant difference in your well-being.
Wearable Tech: How Smart Devices Are Shaping Heart Health
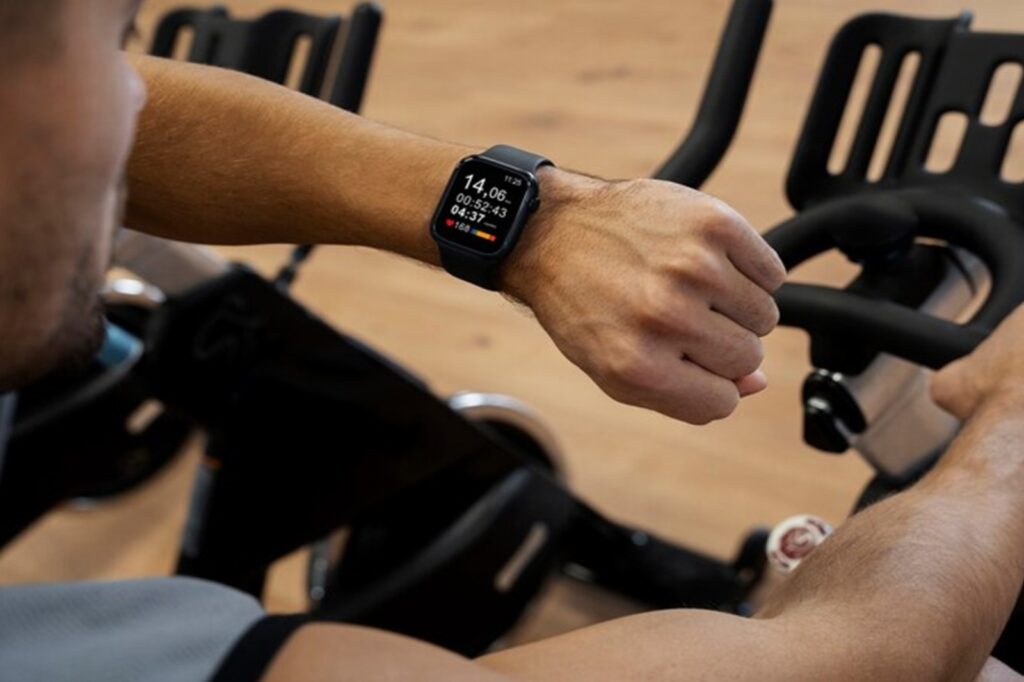

In recent years, wearable technology has revolutionized the way we monitor and manage our health. From fitness trackers to smartwatches, these devices have become integral tools for promoting cardiovascular wellness. Here’s how smart devices are shaping heart health and transforming preventive care: Continuous Monitoring One of the most significant advantages of wearable tech is the ability to continuously monitor heart health metrics in real-time. Devices like the Apple Watch, Fitbit, and Garmin offer features that track heart rate, heart rate variability, and even detect irregular heart rhythms. This constant monitoring allows users to stay informed about their heart health and make timely adjustments to their lifestyle. Early Detection of Irregularities Advanced smartwatches now come equipped with electrocardiogram (ECG) capabilities. These features can detect signs of atrial fibrillation (AFib), a common but serious heart rhythm disorder. Early detection of AFib through wearable devices can prompt users to seek medical advice sooner, potentially preventing serious complications like stroke. Encouraging Physical Activity Wearable devices encourage users to stay active by tracking steps, distance, and calories burned. Many devices set daily activity goals and provide reminders to move if you’ve been sedentary for too long. Regular physical activity is crucial for maintaining cardiovascular health, and these gentle nudges can help users incorporate more movement into their daily routines. Stress Management Chronic stress negatively impacts heart health, contributing to conditions like hypertension and heart disease. Many wearables now include stress-tracking features that monitor physiological signs of stress, such as heart rate variability. Some devices offer guided breathing exercises and relaxation techniques, helping users manage stress effectively. Sleep Quality Monitoring Quality sleep is vital for overall health, including cardiovascular wellness. Wearable tech can track sleep patterns, providing insights into the duration and quality of sleep. By analyzing this data, users can make informed changes to improve their sleep habits, which in turn supports heart health. Health Data Integration Wearable tech often integrates seamlessly with health apps, providing a comprehensive view of your health data. Platforms like Apple Health, Google Fit, and others aggregate data from various sources, offering users and healthcare providers a holistic view of health metrics. This integration can facilitate better-informed decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medical care. Personalized Health Insights The data collected by wearables can be used to generate personalized health insights. By analyzing trends and patterns, these devices can provide tailored recommendations to improve cardiovascular health. For instance, if a wearable detects that a user’s resting heart rate is consistently high, it may suggest lifestyle changes or prompt a visit to a healthcare professional. Research and Development Wearable technology also plays a crucial role in medical research. Aggregated data from millions of users can be used to identify trends, improve understanding of heart disease, and develop new treatments. This vast pool of real-world data is invaluable for advancing cardiovascular research and improving public health strategies. Conclusion Wearable tech is not just a trend; it’s a powerful tool for enhancing heart health. By providing continuous monitoring, early detection of irregularities, and encouraging healthier lifestyles, smart devices are transforming the way we approach cardiovascular wellness. As technology continues to advance, the potential for wearables to improve heart health outcomes will only grow, making them an essential component of modern healthcare. Embrace the future of heart health with wearable technology and take proactive steps towards a healthier heart today.
Understanding Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: A Silent Threat

Introduction: Diabetes is a complex condition that affects more than just blood sugar levels. It can silently threaten another vital organ: the heart. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a lesser-known but significant complication of diabetes that can have serious consequences. In this blog, we’ll explore what diabetic cardiomyopathy is, its causes, symptoms, and ways to manage and prevent it. What is Diabetic Cardiomyopathy? Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a heart condition that occurs in people with diabetes, independent of other heart diseases or risk factors. It primarily affects the structure and function of the heart muscle, leading to problems with pumping blood effectively. Causes of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Glucose Control: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels over time can damage the blood vessels and nerves that control the heart. Inflammation: Diabetes can lead to chronic inflammation in the body, including the heart muscle. Oxidative Stress: High levels of glucose in the blood can lead to oxidative stress, damaging heart cells. Fat Deposits: Diabetes can cause an abnormal buildup of fat in the heart muscle. Symptoms of Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Diabetic cardiomyopathy is often asymptomatic in its early stages, earning it the name “silent threat.” However, as it progresses, it may manifest with symptoms such as: Shortness of breath Swelling in the legs, ankles, or feet (edema) Fatigue Irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) Reduced ability to exercise Increased heart rate Managing and Preventing Diabetic Cardiomyopathy: Blood Sugar Control: Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial in managing and preventing diabetic cardiomyopathy. Regular monitoring and adherence to treatment plans are essential. Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk. This includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, weight management, and stress reduction. Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control: Keep blood pressure and cholesterol levels in check through medication, if necessary, and lifestyle changes. Medication: Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to manage diabetes and heart-related issues effectively. Regular Check-ups: Routine check-ups with your healthcare team can help detect any cardiac issues early, allowing for timely intervention. Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, quitting is critical for heart health. Diabetic cardiomyopathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can affect the heart’s structure and function. Awareness, early detection, and proactive management are essential in preventing its progression. By diligently managing your diabetes, adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, and working closely with your healthcare team, you can reduce the risk of diabetic cardiomyopathy and protect your heart’s health for years to come. Remember that your heart health is as crucial as your blood sugar control in the journey of living well with diabetes.
Lifestyle Changes to Reduce Cardiac Risks in Diabetic Individuals

Introduction: Living with diabetes means adopting a proactive approach to protect your heart. Diabetes is a significant risk factor for heart disease, but the good news is that many of the factors contributing to heart disease are modifiable through lifestyle changes. In this blog, we’ll explore key lifestyle changes that can help reduce cardiac risks in diabetic individuals. 1. Prioritise a Heart-Healthy Diet: A heart-healthy diet is essential for managing diabetes and reducing cardiac risks. Focus on: Fruits and Vegetables: Aim for a variety of colourful produce to ensure a wide range of nutrients. Whole Grains: Choose whole grains like brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat over refined grains. Lean Proteins: Opt for lean sources of protein such as poultry, fish, beans, and legumes. Healthy Fats: Include sources of healthy fats like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Limit Sodium and Added Sugars: Watch your salt and sugar intake, as excessive consumption can harm your heart. 2. Regular Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, manage blood sugar levels, and strengthen your heart. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week. Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are excellent choices. 3. Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for reducing cardiac risks. Even a modest weight loss can have a positive impact on blood sugar control and heart health. Consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider for personalized weight management strategies. 4. Blood Pressure Control: High blood pressure is a significant risk factor for heart disease. Monitor your blood pressure regularly and work with your healthcare team to keep it within a healthy range. Lifestyle changes may include a low-sodium diet, regular exercise, and medication as prescribed. 5. Cholesterol Management: High cholesterol levels can contribute to heart disease. Talk to your doctor about cholesterol-lowering medications if necessary. Additionally, adopt a diet low in saturated and trans fats and high in fiber. 6. Smoking Cessation: If you smoke, quitting is one of the most impactful changes you can make for your heart and overall health. Seek support and resources to help you quit smoking. 7. Stress Reduction: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels and heart health. Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your routine, such as meditation, deep breathing, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. 8. Medication Adherence: If your healthcare provider prescribes medication to manage diabetes or heart-related issues, take them as directed. Skipping doses can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar levels and increased heart risks. 9. Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare team. Monitoring your diabetes, heart health, and overall well-being under professional guidance is essential for early detection and effective management. 10. Stay Informed: Keep yourself informed about the latest research and developments in diabetes and heart disease management. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. Managing diabetes and reducing cardiac risks requires a commitment to a heart-healthy lifestyle. By implementing these lifestyle changes, you can significantly lower your risk of heart disease while improving your overall well-being. Remember that these changes are not one-time efforts but ongoing commitments to a healthier, happier life. Work closely with your healthcare team for guidance and support on your journey to better heart health.
Managing Diabetes: Tips for a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle

Introduction: Living with diabetes means paying extra attention to your heart health. Diabetes and heart disease often go hand in hand, making it essential to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle. Fortunately, there are several strategies you can implement to protect your heart while managing your diabetes effectively. Maintain a Balanced Diet: A heart-healthy diet is a cornerstone of diabetes management. Focus on whole, unprocessed foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit your intake of saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. Watch portion sizes, and consider working with a registered dietitian to create a personalized meal plan. Monitor Blood Sugar Levels: Regularly check your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider. Keeping your blood sugar within a target range can reduce the risk of heart complications associated with diabetes. Stay Physically Active: Incorporate regular exercise into your routine. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with strength training exercises two or more days a week. Exercise can help control blood sugar levels and improve heart health. Manage Your Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce your risk of heart disease. If you’re overweight, even a modest weight loss can have a positive impact on your heart health and diabetes management. Control Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: High blood pressure and cholesterol levels are risk factors for heart disease. Work closely with your healthcare team to monitor and manage these parameters through medication, lifestyle changes, or a combination of both. Don’t Smoke: Smoking increases the risk of heart disease and worsens the complications of diabetes. If you smoke, seek support to quit. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your heart and overall health. Manage Stress: Chronic stress can affect blood sugar levels and heart health. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, or engaging in hobbies you enjoy. Medication Adherence: If prescribed medication for diabetes or heart-related issues, be sure to take them as directed by your healthcare provider. Skipping doses can lead to uncontrolled blood sugar levels and increased heart risks. Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare team. Monitoring your diabetes, heart health, and overall well-being with a healthcare professional’s guidance is crucial for early detection and effective management. Stay Informed: Keep yourself informed about the latest research and developments in diabetes and heart disease management. Knowledge empowers you to make informed decisions about your health. Managing diabetes and maintaining heart health require ongoing commitment and a holistic approach to wellness. By incorporating these tips into your daily life and collaborating closely with your healthcare team, you can reduce the risk of heart complications associated with diabetes and enjoy a heart-healthy lifestyle. Remember that small, sustainable changes can lead to significant improvements in your overall health and well-being.


